Describe the Role of Calcium in Muscle Contraction
Troponin is the sole calcium-binding component of thin filaments actin-tropomyosin-troponin complex of striated muscles. The myosin heads have a molecules of ATP attatched which is hydrolysed into ADP and Pi causing.

Solved Explain The Role Of Calcium Ca2 In The Process Of Chegg Com
During muscle contraction the thin filaments slide over the thick filaments.
. The C a 2 ions bind to the C portion of the actin filament exposing the binding region to which the myosin head is attached to stimulated muscle contraction. From Discovering Nutrition by Paul M. Too much or too little calcium in your blood may cause muscular.
As a muscle action potential travels along the sarcolemma and into the transverse tubule system the ions release channels open in the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. When a muscle fiber is relaxed the concentration of calcium ions is less in the sarcoplasm. In skeletal muscles this excitation-contraction coupling is known as electromechanical release mechanism Because the calcium release channels and the voltage-gated calcium channels are physically coupled.
The heads of the thick myosin filaments in skeletal muscle tissue pull on slide past the thin actin with troponin and tropomyosin filaments during muscle contraction this causes the sarcomere to shorten. In sarcoplasm Ca2 ions attach to one of the three molecules of troponin. The sodium influx also sends a message within the muscle fiber to trigger the release of stored calcium ions.
ATP then binds to myosin moving the myosin to its high-energy state releasing the myosin head from the actin active site. 8 The calcium ions result in movement of troponin and tropomyosin on their thin filaments and this enables the myosin molecule heads to grab and swivel their way along the thin filament. Calcium has a central role in muscle contractions as the flow of calcium ions inside muscle cells causes muscles to contract or relax.
Contraction and relaxation of your muscles occur because of rapidly changing concentrations of calcium inside your muscle cells a biochemical process referred to as the calcium cycle. From sarcoplasmic reticulum these ions Ca2 released into the cytoplasm of the muscle cell specifically called as sarcoplasm. This binding to troponin causes tropomyosin- which at rest blocks the actin-myosin binding sites- moves to expose these binding sites.
Troponin plays a central role in the calcium-regulation of muscle contraction. Thin filaments without troponin support contraction irrespective of calcium concentration. This is the driving force of muscle contraction.
In actin-linked regulation troponin and tropomyosin regulate actin by blocking sites on actin required for complex formation with myosin. Role of Calcium in Muscle Contraction Step 1. These calcium ions bind to the troponin in the muscle filament which causes the exposure of myosin binding sites.
Calcium ions diffuse from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and bind to troponin. As a result calcium ions flood in the sarcoplasm around the thick and thin filaments which in turn binds troponin. In muscle contraction calcium ions play an important role by building interactions between proteins myosin and actin.
Due to its exposure the high-energy myosin head bridg View the full answer. They are smooth muscle skeletal and cardiac. Acetylcholine is released when a neural signal reaches a neuromuscular junction and an action potential is generated in the sarcolemma.
Chimp lifting weights Step 2. Ca ions are pumped back into the SR which causes the tropomyosin to reshield the binding sites on the actin strands. Describe the part played by calcium ions in muscle contraction 2 Moves detaches changes position of shape of switch protein blocking molecule tropomyosin troponin.
Describe the role of calcium ions and ATP during muscle contraction. Action potential reaches muscles cells triggering calcium to be released from sacroplasmic reticulum. What is the role of calcium ions in muscle contraction.
Open channels allow an influx of sodium ions into the cytoplasm of the muscle fiber. Describe the role of calcium in muscle contraction. Calcium triggers contraction by reaction with regulatory proteins that in the absence of calcium prevent interaction of actin and myosin.
Action potential activated Example. The release of calcium ions initiates muscle contractions. In myosin-linked regulation sites on.
A muscle may also stop contracting when it runs out of ATP and becomes fatigued. Insel Jones Bartlett Learning 2013. So the correct option is to bind with troponin changing its shape so that the actin filament is exposed.
Calcium ions released by the sarcoplasmic reticulum play a vital role in contraction of muscles. Relaxation of a Muscle Fiber. As an action potential reaches a muscle cell it triggers calcium to release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of the cells.
The relationship between the chains of proteins within the muscle cells changes leading to the contraction. Action potentials are electrical signals that tell muscle tissue to contract. Calcium ions triggers muscle contraction by binding to the protein complex troponin which in turn exposes the active binding site on the actin.
Two different regulatory systems are found in different muscles. A Calcium plays an essential role in muscle contraction. The short version is that the basic movement of muscle contraction is the head on a myosin filament being activated by ATP and interacting with a binding site on an actin filament which will use this movement to slide.
When this spreads through the muscle fibre calcium. The muscle contraction cycle is triggered by calcium ions binding to the protein complex troponin exposing the active-binding sites on the actin. Uncovering binding site on actin allows cross bridges to form.
Calcium plays a critical role in cardiac muscle contraction because it regulates the position of tropomyosin. The release of calcium helps propagate the muscle contraction and relaxation stages. The calcium ions diffuse into the muscle fiber.
This causes the tropomyosin to displace slightly from the actin filaments. Activates myosin ATP-ase enables myosin head to split ATP. It exposes myosin binding sites on the actin fiber hence allowing myosin heads to form cross bridges with the binding sites on actin.
In the absence of calcium the myosin sites are blocked and the myosin actin interaction cannot happen so neither can the power-stroke and neither. The calcium ions then flow into the cytoplasm and bind to the troponin and. Sets found in the same folder.
No doubt calcium is a key component of strong bones but its presence in your muscles enables movement. A signal sent by the central nervous system via motor neuron initiates muscle contraction. Contraction is turned off by the following sequence of events.
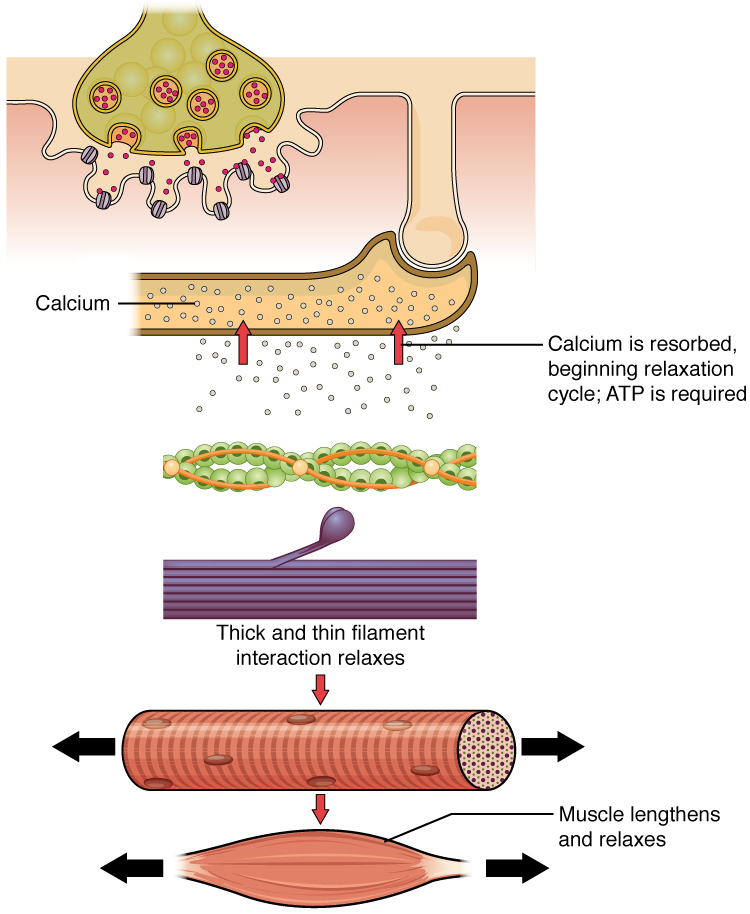
Muscle Fiber Contraction And Relaxation Anatomy And Physiology
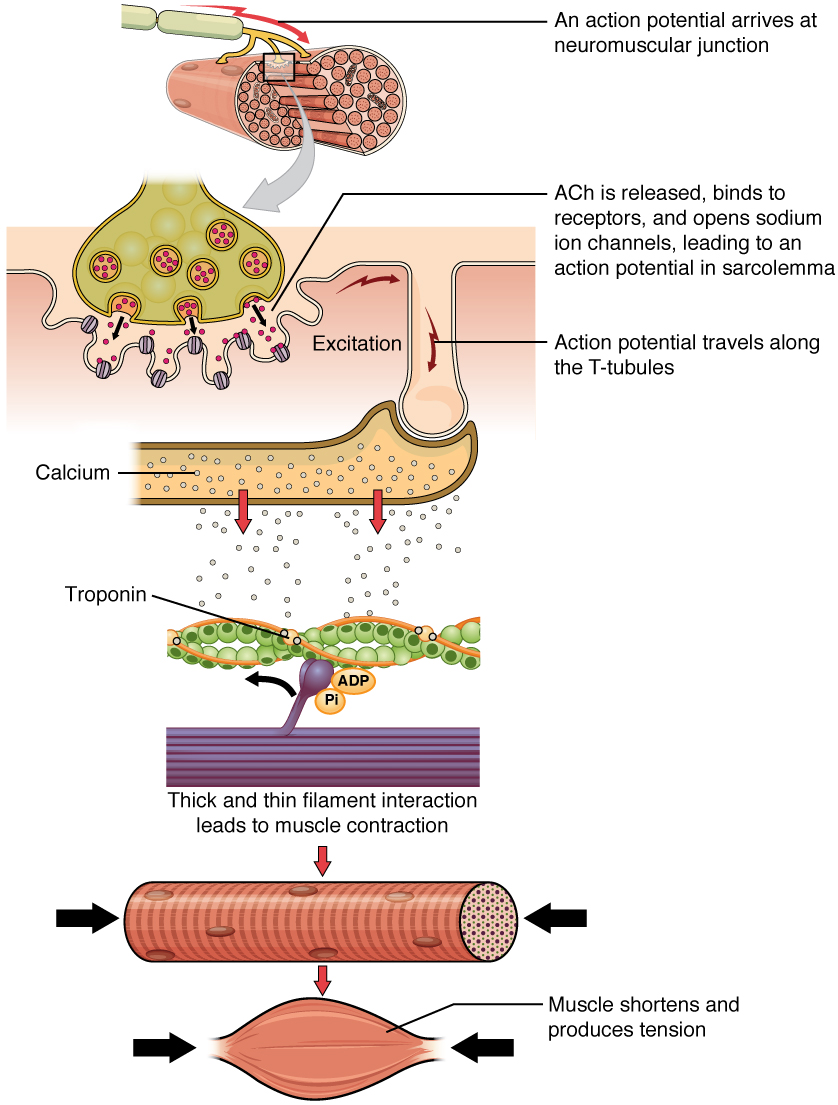
Muscle Fiber Contraction And Relaxation Anatomy And Physiology
Muscle Contraction And Locomotion Boundless Biology
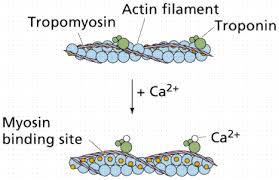
What Function Do Calcium Ions Perform During The Contraction Of Skeletal Muscle Socratic
No comments for "Describe the Role of Calcium in Muscle Contraction"
Post a Comment